tree in bud opacities treatment
When compared to pulmonary tuberculosis upper lobe cavitation is less common and middle lobe bronchiectasis more frequent in Mycobacterium avium complex pulmonary infections. The CT-image shows bronchiectasis bronchial wall thickening and tree-in-bud arrows.
045lu Covid 19 Peripheral Ggo Lungs
Findings consistent with other infections like typical bronchiolitis with tree-in-bud and thickened bronchus walls tbc.

. Some tissue is also present along the blood vessels. The lymphatics first appear in the distal small bronchioles. Can persist for months atelectasis.
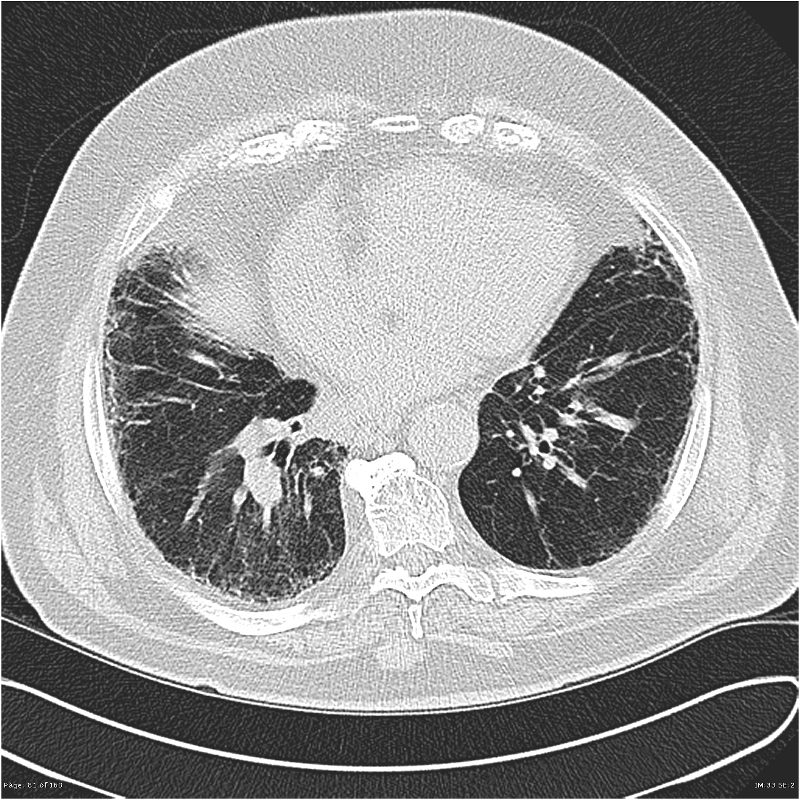
The final diagnosis was Aspergillus bronchiolitis. There are no ground glass opacities. Endobronchial spread along nearby airways is a relatively common finding resulting in relatively well-defined 2-4 mm nodules or branching lesions tree-in-bud sign on CT 13.
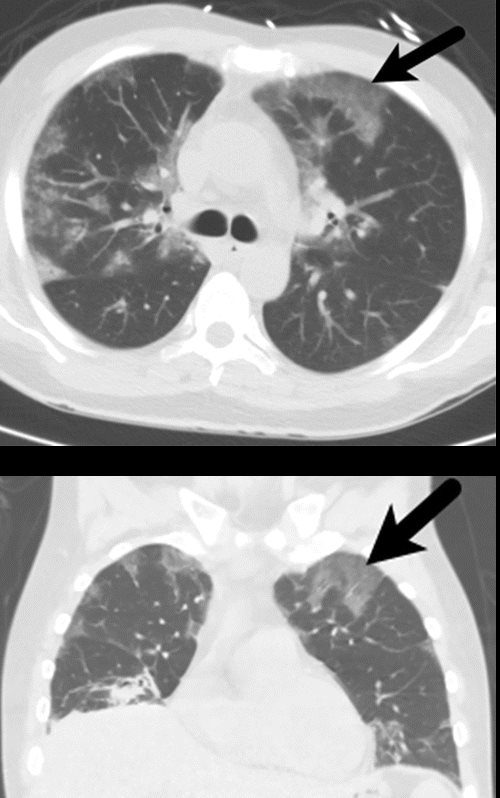
High-resolution CT scan of the thorax demonstrates central bronchiectasis a hallmark of allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis right arrow and the peripheral tree-in-bud appearance of centrilobular opacities left arrow which represent mucoid impaction of the small bronchioles. A high-resolution CT HRCT is more sensitive to changes such as bronchiectasis small nodules tree-in-bud appearance ground glass opacities and pleural thickening. Tiddens HAWM Meerburg JJ.
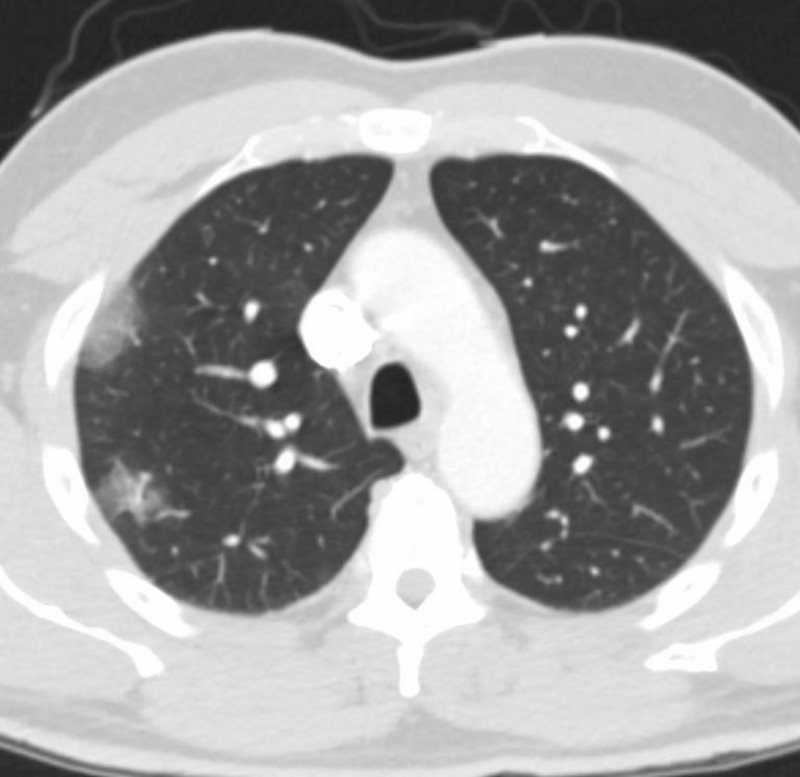
High-resolution computed tomography scan demonstrates thickening of the bronchial and bronchiolar walls and multiple bilateral ill-defined nodular opacities with a tree-in-bud appearance. The lymphoid tissue is involved in both cell mediated as well as antibody mediated immune response. Small patchy peripheral opacities are also present in the left lower lobe.
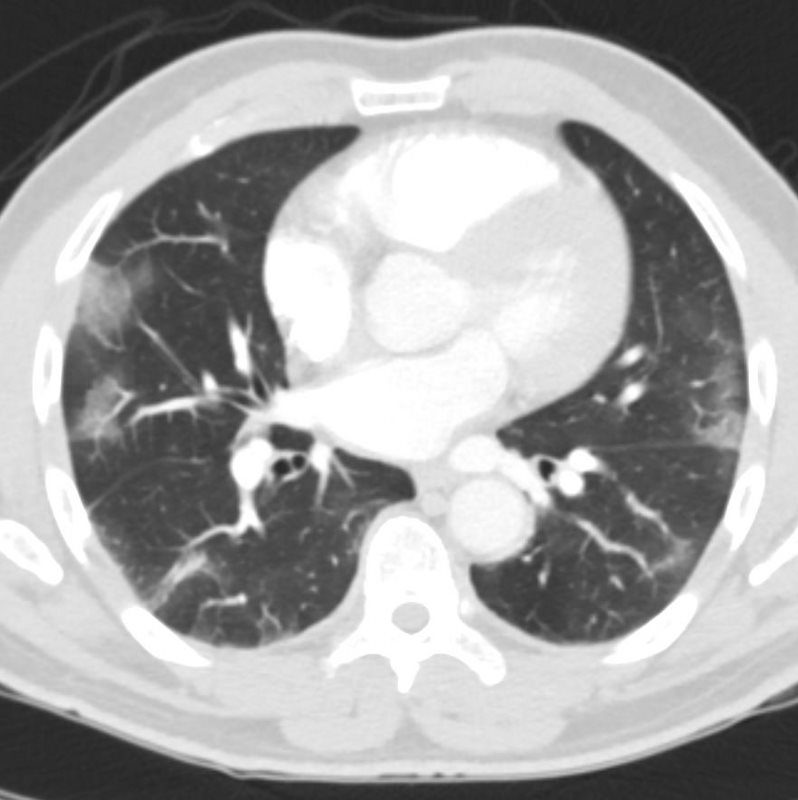
Small nodular densities has been termed tree-in-bud and reflects. The development of an air-fluid level implies communication with the airway and thus the possibility of contagion. Tram line shadows band-like toothpaste shadows finger in glove opacities.
Seen within 6 months after the completion date. The alveoli lack lymphatics. The following criteria apply to symptomatic patients with radiographic opacities nodular or cavitary or an HRCT scan that shows multifocal bronchiectasis with multiple small nodules.
Causes and imaging patterns of tree-in-bud opacities. Treatment of nonpulmonary disease caused by RGM M. An official ATSIDSA statement.
Multiple causes for tree-in-bud TIB opacities have been reported. In the right mid-lung nodular opacities are in a tree-in-bud distribution suggestive of endobronchial spread. A 28-yr-old patient with acute leukaemia presented with fever and a normal chest radiograph.
The differential with superimposed infection should be considered septal thickening may occur later with the alveolar opacities producing a crazy paving pattern 6. Ipsilateral pleural effusion 6. The acute course of COVID-19 is variable and ranges from asymptomatic infection to fulminant respiratory failure.
Is distributed along the tracheobronchial tree. Diagnosis treatment and prevention of nontuberculous mycobacterial diseases published correction appears in Am J Resir Crit Care Med. Patients recovering from COVID-19 can have persistent symptoms and CT abnormalities of variable severity.
Coronal reconstructed computed tomography image shows the lingular cavity with irregular nodules and right mid-lung nodular opacities in a 43-year-old man who. High resolution computed tomography HRCT J Clin Diagn Res 20148RC05 Centrilobular nodules tree in bud pattern mosaic attenuation and mucus impaction. At 3 months after acute infection a subset of patients will have CT abnormalities that include ground-glass opacity GGO and subpleural bands with.
However in rare cases these opacities can also occur with certain autoimmune diseases. However to our knowledge the relative frequencies of the causes have not been evaluated. No typical signs of COVID-19.
Tree-in-bud opacities are frequently caused by infection or aspiration of oropharyngeal or gastric contents. Represents mucoid impaction in dilated bronchi with occlusion of the distal end.
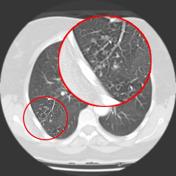
Tree In Bud Sign Lung Radiology Reference Article Radiopaedia Org

Ground Glass Opacification Radiology Reference Article Radiopaedia Org

Review Of The Chest Ct Differential Diagnosis Of Ground Glass Opacities In The Covid Era Abstract Europe Pmc

Ct For Evaluation Of Hemoptysis Radiographics

Tree In Bud Sign Lung Radiology Reference Article Radiopaedia Org
045lu Covid 19 Peripheral Ggo Lungs

The Puncture Needle Is Inserted Into The Lung Parenchyma Until It Download Scientific Diagram

Tree In Bud Sign Lung Radiology Reference Article Radiopaedia Org

Review Of The Chest Ct Differential Diagnosis Of Ground Glass Opacities In The Covid Era Abstract Europe Pmc

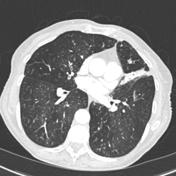
Chest Ct With Multifocal Tree In Bud Opacities Diffuse Bronchiectasis Download Scientific Diagram

Ground Glass Opacification Radiology Reference Article Radiopaedia Org
Tree In Bud Sign Lung Radiology Reference Article Radiopaedia Org
Tree In Bud Sign Lung Radiology Reference Article Radiopaedia Org
Tree In Bud Sign Lung Radiology Reference Article Radiopaedia Org
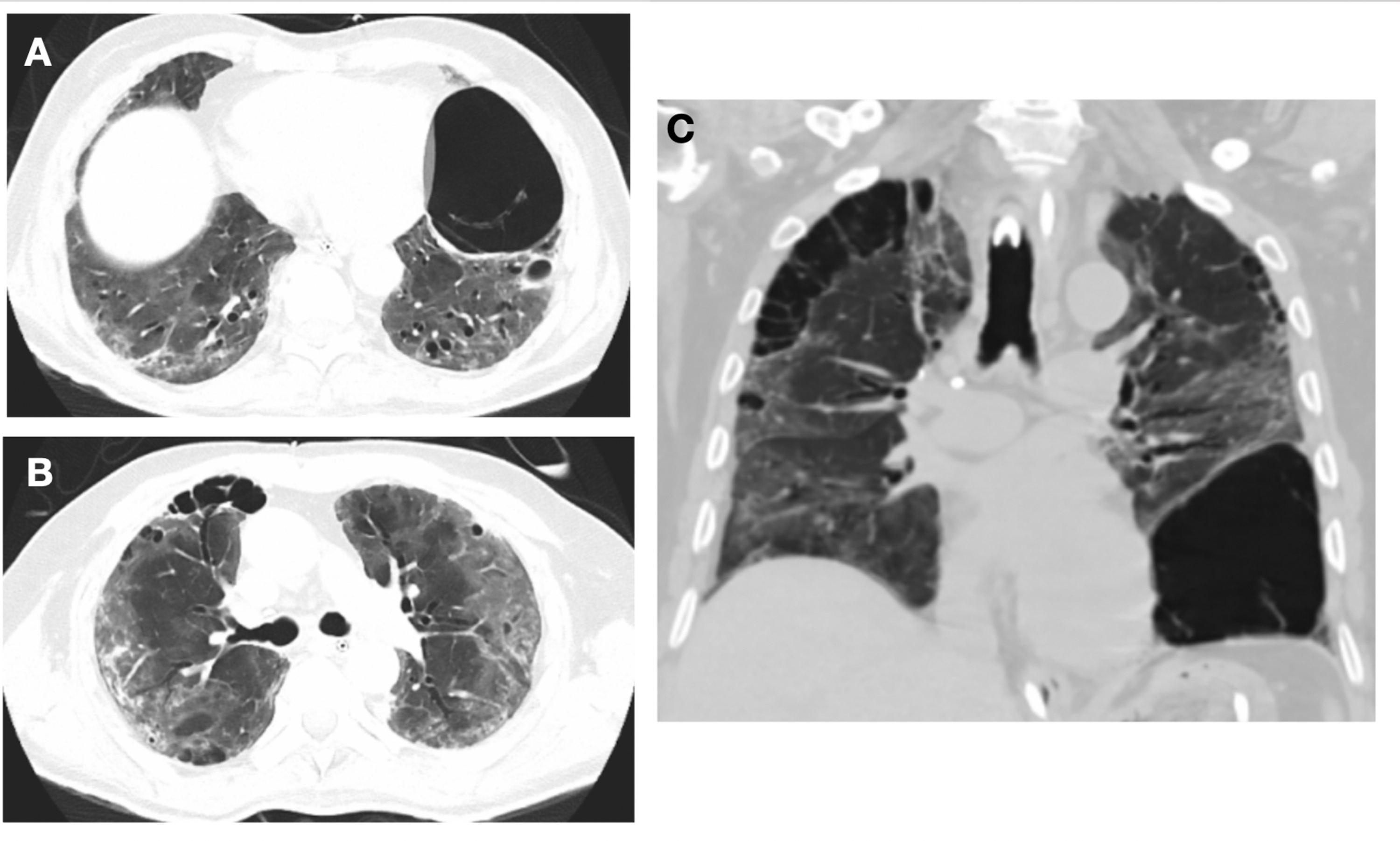
Cureus Pulmonary Cystic Disease Associated With Covid 19 Pneumonia An Emerging Atypical Manifestation

Post Chemotherapy And Targeted Therapy Imaging Of The Chest In Lung Cancer Clinical Radiology